
What is cavitation? What damage does cavitation cause to pumps? How to prevent cavitation?
Cavitation is a phenomenon that can occur in hydraulic machinery and fluid-related systems such as valves and pipelines. The mutual conversion between water and vapor, an inherent property of fluids, requires specific temperature and pressure conditions. For instance, water vaporizes at 100°C under 101325Pa pressure, but only at 30°C under 4243Pa. Similarly, when the temperature remains constant, gradually reducing the absolute pressure at the liquid surface will cause water to vaporize when the pressure drops below a certain threshold. Each pressure level corresponds to a specific vaporization temperature, just as each temperature level corresponds to a specific vaporization pressure. During water flow in a pump, vaporization occurs when the absolute pressure in a localized area drops to or below the vaporization pressure at that temperature, creating numerous bubbles. These bubbles contain steam and active gases like oxygen (O2) that escape from the liquid. When these bubbles reach the high-pressure zone of the pump, the elevated pressure forces them to rapidly deform and collapse. Simultaneously, surrounding fluid particles rush into the bubble's space at extremely high speeds, colliding violently and generating intense water hammer. The larger the bubble, the greater the water hammer pressure during collapse—measured values can reach hundreds or even thousands of megapascals. If bubble collapse occurs near metal surfaces, it creates direct impacts on the material. Continuous bubble formation and collapse result in repeated impacts on metal surfaces, accelerating fatigue-induced erosion. Furthermore, erosion progressively damages the metal protective coating. With the acceleration of condensation heat, reactive gases initiate chemical corrosion, further deteriorating the material. The combined effects of erosion and corrosion transform the metal surface from pitting to honeycomb or sponge-like formations, ultimately leading to complete wall penetration. This entire process of bubble formation, development, collapse, and material failure is collectively termed cavitation.
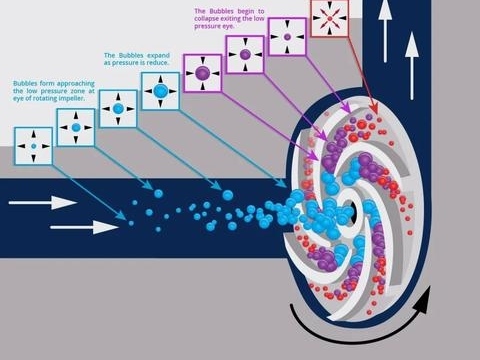
The occurrence and development of cavitation depend on the state of the fluid (temperature, pressure) and the physical properties of the fluid (including the dissolved gas in the impurities).
① Moving cavitation, it refers to the formation of a single transient bubble and small cavities in the fluid, and the growth and collapse of the fluid flow, the cavitation caused by the amount of bubbles, the formation of cloud mist;
② Fixed cavitation, it refers to the cavitation caused by the cavitation attached to the fixed boundary of the flow fluid, also called attached cavitation, in hydraulic machinery this kind of cavitation is the main;
③ Vortex cavitation, it is the bubble produced in the center of the liquid vortex, the speed of the vortex center is large, the pressure is low, easy to make the liquid vaporization cavitation; vibration cavitation, it is the cavitation formed by the continuous high amplitude, high frequency pressure fluctuation in the fluid.
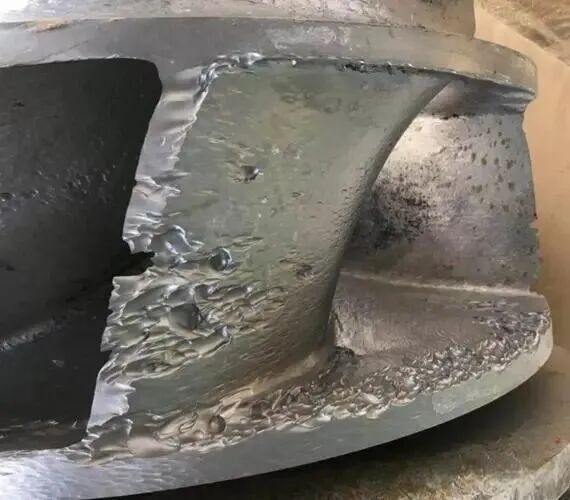


What causes the cavitation of water pump?
● Cavitation is mainly caused by the improper design of pump and system, including unreasonable design of pump inlet pipeline, vortex and slurry disturbance, excessive bubbles entering the pump and high gas content in slurry will also aggravate cavitation.
● Proper design of the pump and system, selection of wear-resistant materials, reduction of air intake into the pump, and proper adjustment of the clearance between the suction side guard plate and the impeller are key measures to minimize cavitation and wear, thereby extending the pump's service life.
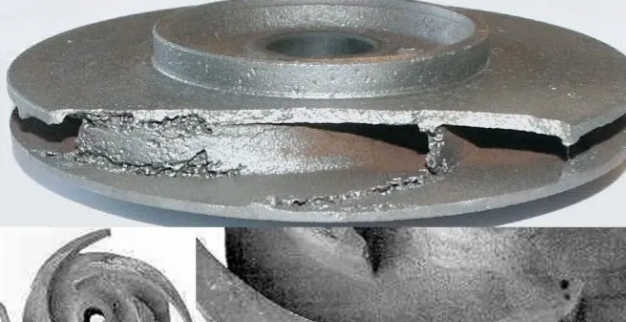
What specific damage can water pump cavitation cause to equipment?
The damage of water pump cavitation to equipment is concentrated in three categories: mechanical damage, performance attenuation and material deterioration.
● Mechanical wear and impact damage
The micro-jet and shock wave produced by the bubble burst will repeatedly impact the impeller, pump shell and other flow components, causing pitting, pitting pits, and in serious cases, forming honeycomb holes or even penetration.
Long-term impact will cause the impeller blade edge peeling and fracture, the pump shell inner wall thinning, and directly damage the structural integrity of the equipment.
● Device performance continues to decline
The cavitation bubbles will occupy the flow channel space, which will cause the actual flow rate, head and efficiency of the pump to decrease significantly, and the pump cannot reach the design working condition.
Bubble blockage in the flow path can cause flow fluctuations and pressure instability, which in turn intensifies pump vibration and affects overall operational stability.
●Material fatigue and corrosion acceleration
Impact load and alternating stress will cause fatigue crack in metal parts, and the crack propagation may lead to the sudden failure of the parts.
Cavitation damages the passivation film on the metal surface, which accelerates the electrochemical corrosion. Especially in the medium containing acid and alkali, corrosion and cavitation promote each other, and further shorten the service life of the equipment.
The most vulnerable area of cavitation in centrifugal pump
●The front cover plate with the maximum impeller curvature is located on the low-pressure side near the blade inlet edge;
The volute tongue and guide vanes in the extrusion chamber are located near the low-pressure side of the inlet edge.
●The sealing clearance between the outer edge of the high specific speed impeller blade tip and the casing, and the low-pressure side of the blade tip without a front cover plate;
The first-stage impeller of a multi-stage pump.
Measures to Improve the Anti-cavitation Performance of Centrifugal Pump
● Optimize the structural design from the pump's suction inlet to the impeller area. Increase the flow cross-sectional area; enhance the curvature radius of the impeller cover's inlet section to mitigate abrupt flow acceleration and pressure drop; reduce the blade inlet thickness appropriately and round the blade inlet to approximate a streamlined profile, which also helps reduce acceleration and pressure drop at the blade leading edge; improve the surface finish of the impeller and blade inlet sections to minimize resistance losses; extend the blade inlet edge toward the impeller inlet to allow earlier fluid work input, thereby increasing pressure.
●The pre-induction wheel is used to make the liquid flow work in advance in the pre-induction wheel, so as to increase the liquid flow pressure.
●The dual-suction impeller design allows liquid to enter from both sides simultaneously, doubling the inlet cross-sectional area while halving the flow velocity.
●. The design condition adopts a slightly larger positive impingement angle to increase the blade inlet angle, reduce the curvature at the blade inlet, minimize blade clogging, thereby enlarging the inlet area; it also improves working conditions under high flow rates to reduce flow loss. However, the positive impingement angle should not be excessively large, as this may affect efficiency.
● Use anti-cavitation material. Practice shows that the higher the strength, hardness and toughness of the material, the better the chemical stability and the stronger the anti-cavitation performance.
Measures to Improve the Effective Cavitation Margin of the Liquid Inlet Device
● Increase the pressure of the liquid level in the pre-pump storage tank to improve the effective cavitation margin.
● Reduce the installation height of the suction device pump.
●Replace the up-pumping device with a backflow device.
● Reduce flow loss in the pipeline before the pump. For example, shorten the pipeline as much as possible within the required range, lower the flow velocity, minimize the use of elbows and valves, and maximize valve opening.
● Reduce the temperature of the working fluid at the pump inlet (when the transported fluid approaches saturation temperature).
The above measures can be applied according to the pump selection, material selection and the pump application site.